Use Edge Browser
How to follow feeds in Microsoft Edge
- Visit the Microsoft Edge Add-on store: https://microsoftedge.microsoft.com/addons/Microsoft-Edge-Extensions-Home. ...
- Search for “rss feed reader”: ...
- Click “Get” Next to “Feeder – RSS Feed Reader”, then Confirm by clicking “Add Extension”
- Setup your feeds: Search for feeds one-by-one, browse the library of sites or import feeds with OP
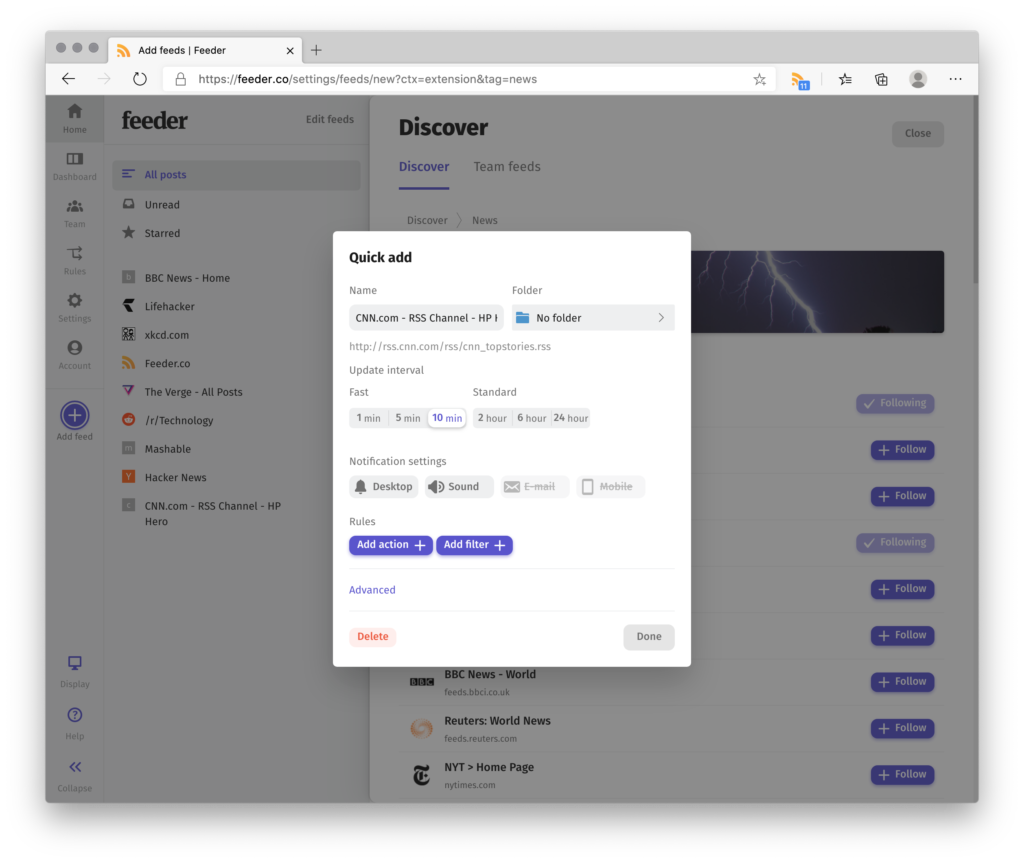
Use Outlook
-
In Outlook, right-click the RSS Feeds folder and choose Add a New RSS Feed.
-
In the New RSS Feed dialog box, enter the URL of the RSS Feed.
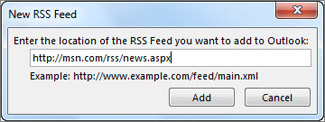
Tip: If you need help finding the RSS feed URL on a website, look for an RSS icon.
 Right-click that icon, and then copy the shortcut to the Clipboard.
Right-click that icon, and then copy the shortcut to the Clipboard.
Press Ctrl+V to paste the information from the Clipboard into the RSS Feed location box.
Choose Add > OK.
Additional Subscription Information: Microsoft How to Subscribe to RSS feed in Outlook
Use Internet Explorer
Open Internet explorer and open any USACE website. Look for the small RSS icon and click on that icon as show in this image:
Once it opens in Internet Explorer, it will have an option at the top to subscribe to this RSS feed as show here:


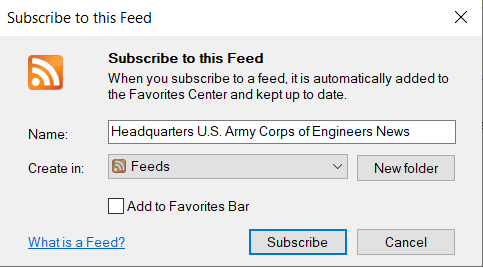
Use Google Chrome
Chrome Extension allows RSS Feed Subscriptions
Free RSS Feed Reader: https://feeder.co